本文已收录到:清华大学操作系统课程实验 专题
练习0:填写已有实验
本实验依赖实验1/2/3。请把你做的实验1/2/3的代码填入本实验中代码中有“LAB1”,“LAB2”,“LAB3”的注释相应部分。
Lab1中需要合并的文件:
-
kdebug.c 中函数print_stackframe
-
kern/trap/trap.c 中对中断向量表进行初始化的函数idt_init
-
trap.c 中的中断处理函数trap(不加)
Lab2中需要合并的文件:
-
default_pmm.c::
-
default_init_memmap
-
default_alloc_pages
-
default_free_pages
-
-
kern/mm/pmm.c::get_pte函数
-
kern/mm/pmm.c中的page_remove_pte函数
Lab3中需要合并的文件:
-
vmm.c::do_pgfault
-
kern/mm/swap_fifo.c::
-
_fifo_map_swappable
-
_fifo_swap_out_victim
-
合并之后运行lab4:

练习1:分配并初始化一个进程控制块(需要编码)
alloc_proc函数(位于kern/process/proc.c中)负责分配并返回一个新的struct proc_struct结构,用于存储新建立的内核线程的管理信息。ucore需要对这个结构进行最基本的初始化,你需要完成这个初始化过程。
【提示】在alloc_proc函数的实现中,需要初始化的proc_struct结构中的成员变量至少包括:state/pid/runs/kstack/need_resched/parent/mm/context/tf/cr3/flags/name。
答:
// alloc_proc - alloc a proc_struct and init all fields of proc_struct static struct proc_struct * alloc_proc(void) { struct proc_struct *proc = kmalloc(sizeof(struct proc_struct)); if (proc != NULL) { //LAB4:EXERCISE1 YOUR CODE /* * below fields in proc_struct need to be initialized * enum proc_state state; // Process state * int pid; // Process ID * int runs; // the running times of Proces * uintptr_t kstack; // Process kernel stack * volatile bool need_resched; // bool value: need to be rescheduled to release CPU? * struct proc_struct *parent; // the parent process * struct mm_struct *mm; // Process's memory management field * struct context context; // Switch here to run process * struct trapframe *tf; // Trap frame for current interrupt * uintptr_t cr3; // CR3 register: the base addr of Page Directroy Table(PDT) * uint32_t flags; // Process flag * char name[PROC_NAME_LEN + 1]; // Process name */ proc->state = PROC_UNINIT; // 进程状态:未初始化 proc->pid = -1; // 未分配的进程pid是-1 先设置pid为无效值-1,用户调完alloc_proc函数后再根据实际情况设置pid。 proc->runs = 0; proc->kstack = 0; // 内核栈位置 proc->need_resched = 0; // 是否需要调度 proc->parent = NULL; // 父进程 proc->mm = NULL; // 虚拟内存结构体(lab4实验可忽略) /* * void *memset(void *s, int c, unsigned long n) * 函数解释:将s中当前位置后面的n个字节 (typedef unsigned int size_t )用 ch 替换并返回 s * 该函数用于清空一个结构体中所有的成员变量,下面解释三个参数: * 第一个参数:位置指针,例如数组名、结构体首地址 * 第二个参数:替换为什么 * memset 函数的第三个参数 n 的值一般用 sizeof() 获取 */ memset(&proc->context, 0, sizeof(struct context)); // 上下文结构体 proc->tf = NULL; proc->cr3 = boot_cr3; proc->flags = 0; // 清空数组就不用sizeof了,第三个参数直接写数组的大小-1即可 memset(&proc->name, 0, PROC_NAME_LEN); } return proc; }
请在实验报告中简要说明你的设计实现过程。请回答如下问题:
-
请说明proc_struct中
struct context context和struct trapframe *tf成员变量含义和在本实验中的作用是啥?(提示通过看代码和编程调试可以判断出来)
答:
注意:这里是初始化进程控制块,而不是创建进程。
struct context context,通过查看context结构体:
struct context { uint32_t eip; uint32_t esp; uint32_t ebx; uint32_t ecx; uint32_t edx; uint32_t esi; uint32_t edi; uint32_t ebp; };
可以发现,context保存的是寄存器信息。
struct trapframe *tf,结构体trapframe:
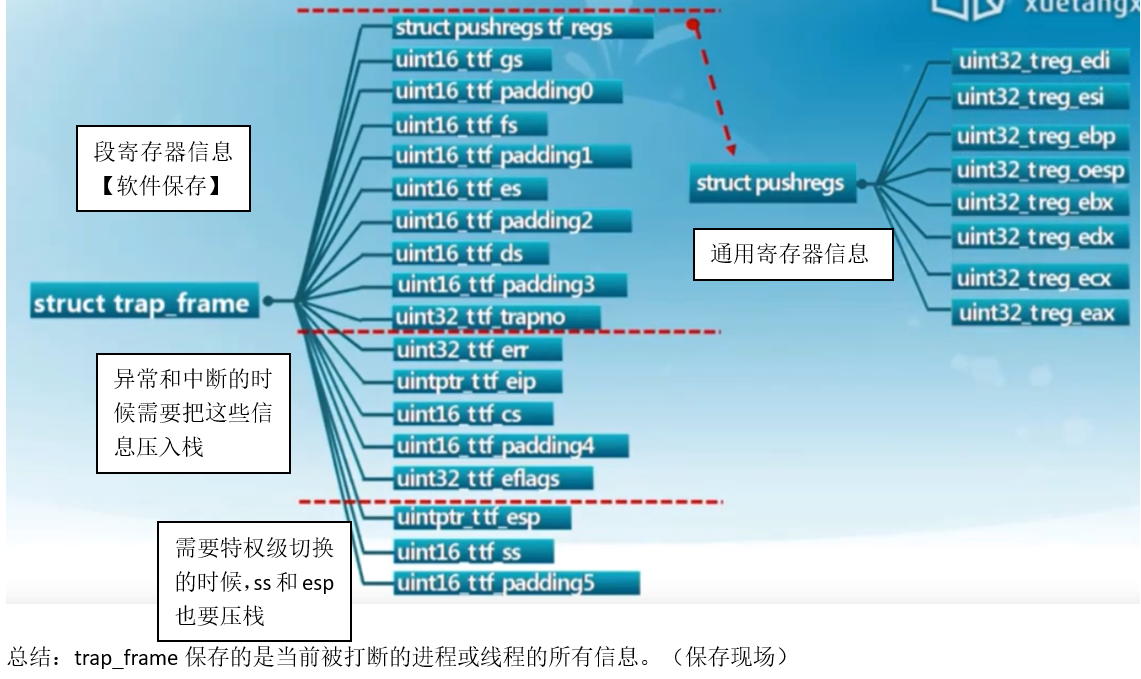
struct trapframe { /* 段寄存器信息 */ struct pushregs tf_regs; uint16_t tf_gs; uint16_t tf_padding0; uint16_t tf_fs; uint16_t tf_padding1; uint16_t tf_es; uint16_t tf_padding2; uint16_t tf_ds; uint16_t tf_padding3; uint32_t tf_trapno; /* below here defined by x86 hardware */ /* 异常和中断时候需要把下列信息压栈 */ uint32_t tf_err; uintptr_t tf_eip; uint16_t tf_cs; uint16_t tf_padding4; uint32_t tf_eflags; /* below here only when crossing rings, such as from user to kernel */ /* 需要特权级转换的时候,下列信息压栈 */ uintptr_t tf_esp; uint16_t tf_ss; uint16_t tf_padding5; } __attribute__((packed));
使用命令查询涉及到 context 的文件行号,找到相关的代码:
[root@wuseyukui]# grep -rn "context" * 说明: -r 是递归查找 -n 是显示行号 * : 表示当前目录所有文件,也可以是某个文件名
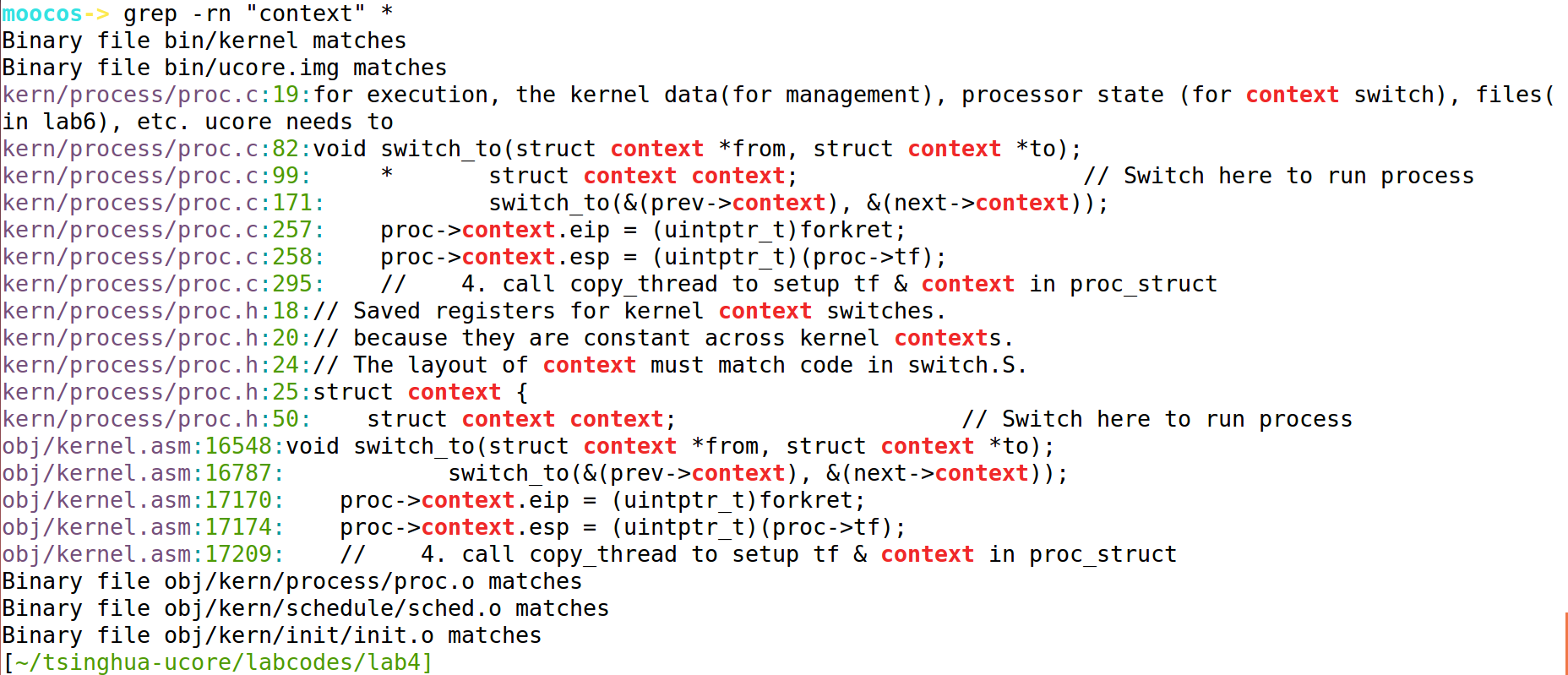
对context结构体进行设置的代码:
kern/process/proc.c:257: proc->context.eip = (uintptr_t)forkret; kern/process/proc.c:258: proc->context.esp = (uintptr_t)(proc->tf);
obj/kernel.asm:17170: proc->context.eip = (uintptr_t)forkret; obj/kernel.asm:17174: proc->context.esp = (uintptr_t)(proc->tf);
在kernel.asm文件的16787行的 switch_to 函数用于执行上下文切换:
obj/kernel.asm:16787: switch_to(&(prev->context), &(next->context));
switch_to 函数的具体汇编代码意义以及保存现场恢复现场实现请参考word笔记和视频P61讲。
练习2:为新创建的内核线程分配资源(需要编码)
创建一个内核线程需要分配和设置好很多资源。kernel_thread函数通过调用do_fork函数完成具体内核线程的创建工作。do_kernel函数会调用alloc_proc函数来分配并初始化一个进程控制块,但alloc_proc只是找到了一小块内存用以记录进程的必要信息,并没有实际分配这些资源。ucore一般通过do_fork实际创建新的内核线程。do_fork的作用是,创建当前内核线程的一个副本,它们的执行上下文、代码、数据都一样,但是存储位置不同。在这个过程中,需要给新内核线程分配资源,并且复制原进程的状态。你需要完成在kern/process/proc.c中的do_fork函数中的处理过程。它的大致执行步骤包括:
-
调用alloc_proc,首先获得一块用户信息块。
-
为进程分配一个内核栈。
-
复制原进程的内存管理信息到新进程(但内核线程不必做此事)
-
复制原进程上下文到新进程
-
将新进程添加到进程列表
-
唤醒新进程
-
返回新进程号
答:
首先,先回看word笔记“进程创建”这一讲。会发现创建新进程需要做下面的工作基本都是复制父进程。只有pid号改变了。
看函数调用图:
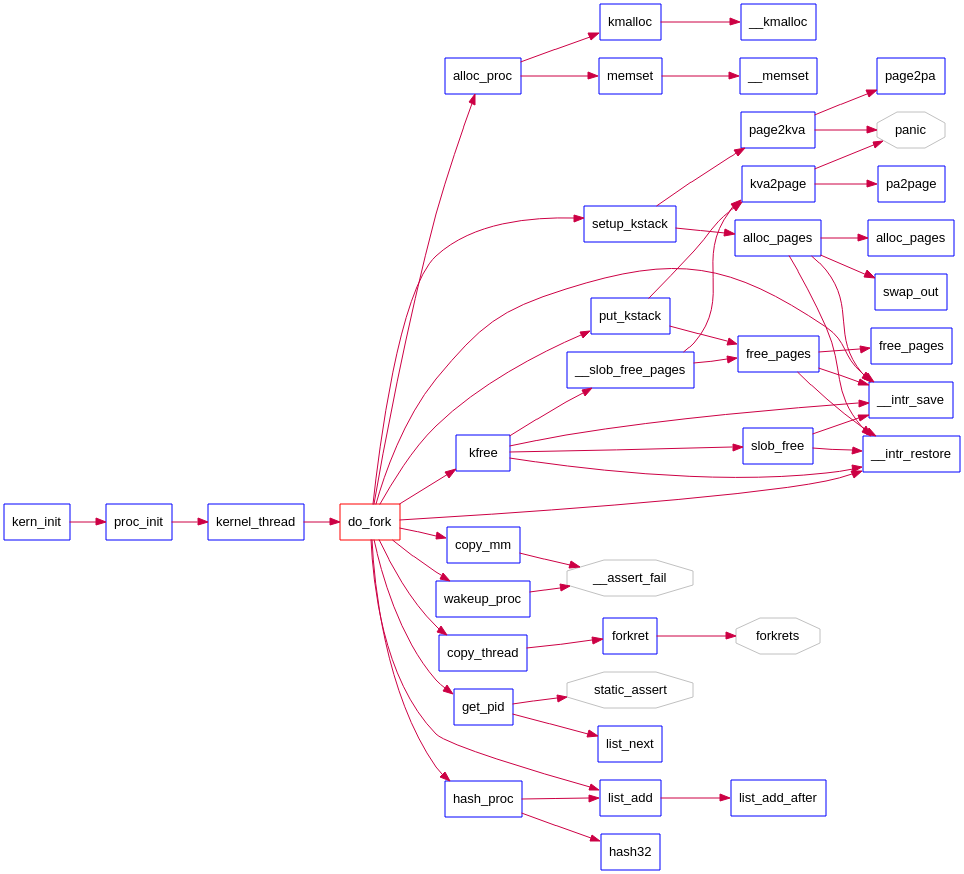
kern/process/proc.c::do_fork
int do_fork(uint32_t clone_flags, uintptr_t stack, struct trapframe *tf) { int ret = -E_NO_FREE_PROC; struct proc_struct *proc; if (nr_process >= MAX_PROCESS) { goto fork_out; } ret = -E_NO_MEM; //LAB4:EXERCISE2 YOUR CODE /* * Some Useful MACROs, Functions and DEFINEs, you can use them in below implementation. * MACROs or Functions: * alloc_proc: create a proc struct and init fields (lab4:exercise1) * setup_kstack: alloc pages with size KSTACKPAGE as process kernel stack * copy_mm: process "proc" duplicate OR share process "current"'s mm according clone_flags * if clone_flags & CLONE_VM, then "share" ; else "duplicate" * copy_thread: setup the trapframe on the process's kernel stack top and * setup the kernel entry point and stack of process * hash_proc: add proc into proc hash_list * get_pid: alloc a unique pid for process * wakup_proc: set proc->state = PROC_RUNNABLE * VARIABLES: * proc_list: the process set's list * nr_process: the number of process set */ // 1. call alloc_proc to allocate a proc_struct // 2. call setup_kstack to allocate a kernel stack for child process // 3. call copy_mm to dup OR share mm according clone_flag // 4. call copy_thread to setup tf & context in proc_struct // 5. insert proc_struct into hash_list && proc_list // 6. call wakup_proc to make the new child process RUNNABLE // 7. set ret vaule using child proc's pid /* * 想干的事:创建当前内核线程的一个副本,它们的执行上下文、代码、数据都一样,但是存储位置不同,PID不同。 */ // 调用alloc_proc() 为要创建的线程分配空间 // 如果第一步 alloc 都失败的话,应该来说是比较严重的错误。直接退出。 if ((proc = alloc_proc()) == NULL) { goto fork_out; } // 获取被拷贝的进程的pid号 即父进程的pid //proc->parent = current; // 分配大小为 KSTACKPAGE 的页面作为进程内核堆栈 setup_kstack(proc); // 拷贝原进程的内存管理信息到新进程 copy_mm(clone_flags, proc); // 拷贝原进程上下文到新进程 copy_thread(proc, stack, tf); bool intr_flag; // 停止中断 local_intr_save(intr_flag); // {} 用来限定花括号中变量的作用域,使其不影响外面。 { proc->pid = get_pid(); // 新进程添加到 hash方式组织的的进程链表,以便于以后对某个指定的线程的查找(速度更快) hash_proc(proc); // 将线程加入到所有线程的链表中,以便于调度 list_add(&proc_list, &(proc->list_link)); // 将全局线程的数目加1 nr_process ++; } // 允许中断 local_intr_restore(intr_flag); // 唤醒新进程 wakeup_proc(proc); // 新进程号 ret = proc->pid; fork_out: return ret; bad_fork_cleanup_kstack: put_kstack(proc); bad_fork_cleanup_proc: kfree(proc); goto fork_out; }
请在实验报告中简要说明你的设计实现过程。请回答如下问题:
-
请说明ucore是否做到给每个新fork的线程一个唯一的id?请说明你的分析和理由。
答:
一方面,从上面的代码可以看出。在分配PID之前禁止了中断,然后再分配OK后允许中断。相当于事务的隔离性。
查看pid分配函数 proc.c::get_pid:
static int get_pid(void) { static_assert(MAX_PID > MAX_PROCESS); struct proc_struct *proc; list_entry_t *list = &proc_list, *le; // 两个静态变量 next_safe = MAX_PID, last_pid = MAX_PID; 指向最大可以分配的pid号码 static int next_safe = MAX_PID, last_pid = MAX_PID; if (++ last_pid >= MAX_PID) { last_pid = 1; goto inside; } if (last_pid >= next_safe) { inside: next_safe = MAX_PID; repeat: le = list; while ((le = list_next(le)) != list) { proc = le2proc(le, list_link); if (proc->pid == last_pid) { // 如果last_pid+1 后等于MAX_PID,意味着pid已经分配完了 if (++ last_pid >= next_safe) { // 如果last_pid超出最大pid范围,则last_pid重新从1开始编号 if (last_pid >= MAX_PID) { last_pid = 1; } next_safe = MAX_PID; // 重新编号去 现在 last_pid == 1; next_safe == MAX_PID; goto repeat; } } // 上面的是需要重新编号的情况,下面是不需要的情况 // 满足 last_pid < proc->pid < next_safe else if (proc->pid > last_pid && next_safe > proc->pid) { // last_pid < proc->pid < next_safe // last_pid < proc->pid // < next_safe next_safe = proc->pid; } } } // last_pid作为新颁发的编号 return last_pid; }
注释很明确的说明了原因:分为需要从1开始编号的情况和无需重新编号共计两种情况。
练习3:阅读代码,理解 proc_run 函数和它调用的函数如何完成进程切换的。(无编码工作)
请在实验报告中简要说明你对proc_run函数的分析。并回答如下问题:
答:
先搜下proc_run函数在哪被调用过:
moocos-> grep -rn “proc_run” * Binary file bin/kernel matches Binary file bin/ucore.img matches kern/schedule/sched.c:40: proc_run(next); kern/process/proc.c:33: + + proc_run + kern/process/proc.c:207:// proc_run – make process “proc” running on cpu kern/process/proc.c:210:proc_run(struct proc_struct *proc) { kern/process/proc.h:65:void proc_run(struct proc_struct *proc); obj/kernel.asm:16746:c0108839 <proc_run>: obj/kernel.asm:16748:// proc_run – make process “proc” running on cpu obj/kernel.asm:16751:proc_run(struct proc_struct *proc) { obj/kernel.asm:16758:c0108847: 74 63 je c01088ac <proc_run+0x73> obj/kernel.asm:17823: proc_run(next); obj/kernel.asm:17826:c0109072: e8 c2 f7 ff ff call c0108839 <proc_run> obj/kernel.sym:563:c0108839 proc_run Binary file obj/kern/schedule/sched.o matches Binary file obj/kern/process/proc.o matches
发现在 schedule/sched.c::schedule函数中被调用过:
if (next != current) { // 交给CPU去执行 proc_run(next); }
proc_run(next)函数:
void proc_run(struct proc_struct *proc) { // current是当前正在运行的线程 // proc是将要运行的线程 /* 先判断下将要运行的线程是不是已经在运行中了 */ if (proc != current) { bool intr_flag; // prev是当前正在执行的线程 // next是准备要执行的线程 struct proc_struct *prev = current, *next = proc; // 禁止中断 目的是事务的隔离性 不让其冲突 local_intr_save(intr_flag); { current = proc; load_esp0(next->kstack + KSTACKSIZE); // 将当前的cr3寄存器修改为需要运行的线程(线程)的页目录表 lcr3(next->cr3); // 开始执行(切换线程函数) switch_to(&(prev->context), &(next->context)); } local_intr_restore(intr_flag); } }
然后就可以去执行线程了。
-
在本实验的执行过程中,创建且运行了几个内核线程?
答:
第0个内核线程 — idleproc:最初的内核线程
第1个内核线程init_main:打印字符串用的
-
语句
local_intr_save(intr_flag);....local_intr_restore(intr_flag);在这里有何作用?请说明理由答:
上面一题已解答。作用就是先禁止中断,执行完下面代码后再允许中断。——避免事务冲突。
current = proc; load_esp0(next->kstack + KSTACKSIZE); lcr3(next->cr3); switch_to(&(prev->context), &(next->context));
完成代码编写后,编译并运行代码:make qemu
如果可以得到如 附录A所示的显示内容(仅供参考,不是标准答案输出),则基本正确。
参考文献
https://www.jianshu.com/p/50dd281a82f0
https://blog.csdn.net/tangyuanzong/article/details/78692050
https://blog.csdn.net/wuseyukui/article/details/84138443