本文已收录到:清华大学操作系统课程实验 专题
练习0:填写已有实验
本实验依赖实验1。请把你做的实验1的代码填入本实验中代码中有“LAB1”的注释相应部分。提示:可采用diff和patch工具进行半自动的合并(merge),也可用一些图形化的比较/merge工具来手动合并,比如meld,eclipse中的diff/merge工具,understand中的diff/merge工具等。
Lab1中需要合并的文件:
-
kdebug.c中函数print_stackframe
-
kern/trap/trap.c中对中断向量表进行初始化的函数idt_init
-
trap.c中的中断处理函数trap
练习1:实现 first-fit 连续物理内存分配算法(需要编程)
在实现first fit 内存分配算法的回收函数时,要考虑地址连续的空闲块之间的合并操作。提示:在建立空闲页块链表时,需要按照空闲页块起始地址来排序,形成一个有序的链表。可能会修改default_pmm.c中的default_init,default_init_memmap,default_alloc_pages, default_free_pages等相关函数。请仔细查看和理解default_pmm.c中的注释。
首先根据练习1的要求,在default_pmm.c文件注释中要求重写
-
default_init,
-
default_init_memmap(需要重写),
-
default_alloc_pages(需要重写),
-
default_free_pages (需要重写)
4个函数。
first-fit连续物理内存分配算法大概思路:分配n个字节,使用第一个可用空间比n大的空闲块。
首先,针对内存,分为下面的几大模块:
-
探测物理内存
-
物理内存管理的初始化
-
内存段页式管理
-
地址映射
-
自映射
可参考这里写的探测内存的方法:https://twinkle0331.github.io/ucore-lab2.html
当我们在bootloader中完成对物理内存空间的探测后, 我们就可以根据得到的信息来对可用的内存空间进行管理。在ucore中, 我们将物理内存空间按照页的大小(4KB)进行管理, 页的信息用Page这个结构体来保存。下面是Page在Lab2中的具体描述:
kern/mm/memlayout.h:
struct Page { int ref; // 映射此物理页的虚拟页个数 uint32_t flags; // 物理页的状态标记 unsigned int property; // 空闲时,代表以此为首的连续空闲页的数量 list_entry_t page_link; // 把多个连续内存空闲块链接在一起的双向链表指针 };
ref:映射此物理页的虚拟页个数。一旦某页表中有一个页表项设置了虚拟页到这个Page管理的物理页的映射关系,就会把Page的ref加一。反之,若是解除,那就减一。
flags:表示此物理页的状态标记,有两个标志位,第一个表示是否被保留,如果被保留了则设为1(比如内核代码占用的空间)。第二个表示此页是否是free的。如果设置为1,表示这页是free的,可以被分配;如果设置为0,表示这页已经被分配出去了,不能被再二次分配。
property:记录某连续内存空闲块的大小。
page_link:是便于把多个连续内存空闲块链接在一起的双向链表指针,连续内存空闲块利用这个页的成员变量 page_link 来链接比它地址小和大的其他连续内存空闲块。
libs/list.h 双向链表:
双向链表在 libs/list.h 结构体定义并提供基本操作函数:
struct list_entry { struct list_entry *prev, *next; }; typedef struct list_entry list_entry_t; static inline void list_init(list_entry_t *elm) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline void list_add(list_entry_t *listelm, list_entry_t *elm) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline void list_add_before(list_entry_t *listelm, list_entry_t *elm) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline void list_add_after(list_entry_t *listelm, list_entry_t *elm) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline void list_del(list_entry_t *listelm) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline void list_del_init(list_entry_t *listelm) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline bool list_empty(list_entry_t *list) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline list_entry_t *list_next(list_entry_t *listelm) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline list_entry_t *list_prev(list_entry_t *listelm) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline void __list_add(list_entry_t *elm, list_entry_t *prev, list_entry_t *next) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline void __list_del(list_entry_t *prev, list_entry_t *next) __attribute__((always_inline));
kern/mm/memlayout.h:
/* free_area_t - maintains a doubly linked list to record free (unused) pages */ typedef struct { list_entry_t free_list; // 是一个双向链表的指针 unsigned int nr_free; // 当前空闲页的个数 } free_area_t;
free_list:list_entry_t 是一个双向链表,所以 list_entry_t free_list 是一个 list_entry 结构的双向链表指针。 nr_free:记录当前空闲页的个数。
先来看 default_pmm.c::default_init :
// 初始化空闲页块链表 static void default_init(void) { list_init(&free_list); nr_free = 0; // 一开始空闲块是0个 }
初始化free_list并将nr_free设置为0。free_list用于记录空闲的mem块。nr_free是空闲mem块的总数。
default_init函数已经完成,我们不需要操作。
default_pmm.c::default_init_memmap:
* (3) default_init_memmap: CALL GRAPH: kern_init --> pmm_init-->page_init-->init_memmap--> pmm_manager->init_memmap * This fun is used to init a free block (with parameter: addr_base, page_number). * First you should init each page (in memlayout.h) in this free block, include: * p->flags should be set bit PG_property (means this page is valid. In pmm_init fun (in pmm.c), * the bit PG_reserved is setted in p->flags) * if this page is free and is not the first page of free block, p->property should be set to 0. * if this page is free and is the first page of free block, p->property should be set to total num of block. * p->ref should be 0, because now p is free and no reference. * We can use p->page_link to link this page to free_list, (such as: list_add_before(&free_list, &(p->page_link)); ) * Finally, we should sum the number of free mem block: nr_free+=n
// 初始化n个空闲页块 static void default_init_memmap(struct Page *base, size_t n) { assert(n > 0); // 断言需要分配的内存块大小n大于0 struct Page *p = base; // 将每个空闲页初始化并连接 for (; p != base + n; p ++) { assert(PageReserved(p)); // 断言页被内核所保留,???不太懂 p->flags = 0; // 把这个连续空闲块的flags都设置为0 p->property = 0; // 再把这个连续空闲块的property都设置为0 set_page_ref(p, 0); // 清除引用该物理页的引用数 SetPageProperty(p); // 置1:所有空闲页第1位也就是PG_property位置为1 // 头插法 list_add_before(&free_list, &(p->page_link)); } base->property = n;// 对整块的第1个页面,其property属性记录的是连续空闲页的数量 nr_free += n; // 空闲页个数 }

default_pmm.c::default_alloc_pages
* (4) default_alloc_pages: search find a first free block (block size >=n) in free list and reszie the free block, return the addr * of malloced block. * (4.1) So you should search freelist like this: * list_entry_t le = &free_list; * while((le=list_next(le)) != &free_list) { * …. * (4.1.1) In while loop, get the struct page and check the p->property (record the num of free block) >=n? * struct Page *p = le2page(le, page_link); * if(p->property >= n){ … * (4.1.2) If we find this p, then it’ means we find a free block(block size >=n), and the first n pages can be malloced. * Some flag bits of this page should be setted: PG_reserved =1, PG_property =0 * unlink the pages from free_list * (4.1.2.1) If (p->property >n), we should re-caluclate number of the the rest of this free block, * (such as: le2page(le,page_link))->property = p->property – n;) * (4.1.3) re-caluclate nr_free (number of the the rest of all free block) * (4.1.4) return p * (4.2) If we can not find a free block (block size >=n), then return NULL
static void default_init_memmap(struct Page *base, size_t n) { assert(n > 0); struct Page *p = base; for (; p != base + n; p ++) { assert(PageReserved(p)); p->flags = p->property = 0; set_page_ref(p, 0); SetPageProperty(p); list_add_before(&free_list, &(p->page_link)); } base->property = n; nr_free += n; } static struct Page * default_alloc_pages(size_t n) { assert(n > 0); if (n > nr_free) { return NULL; } list_entry_t *len; // 跟以前的p和q双指针差不多,le相当于前指针,len后指针 list_entry_t *le = &free_list; while ((le = list_next(le)) != &free_list) { struct Page *p = le2page(le, page_link); if (p->property >= n) { // 分配页数 int i; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { len = list_next(le); struct Page *pp = le2page(le, page_link); // 每一页的标志位改写 // 被内核所保留 SetPageReserved(pp); // 不是头页 ClearPageProperty(pp); // 既然分配好了,下一步就将其从freelist中删除 list_del(le); le = len; } if (p->property > n) { // p指针移动到顶部(这里好象是反着的,其实到了头页) // 修改头页的标志位,可参考高书8.3.2 //struct Page *p = le2page(le, page_link); le2page(le, page_link)->property = p->property - n; } // 修改头页的标志位 ClearPageProperty(p); SetPageReserved(p); nr_free -= n; return p; } } return NULL; }
default_pmm.c::default_free_pages
(5) default_free_pages: relink the pages into free list, maybe merge(合并) small free blocks into big free blocks.
(5.1) according the base addr of withdrawed blocks(取消的块), search free list, find the correct position
(from low to high addr), and insert the pages. (may use list_next, le2page, list_add_before)
(5.2) reset the fields of pages(页标志), such as p->ref, p->flags (PageProperty)
(5.3) try to merge low addr or high addr blocks. Notice: should change some pages’s p->property correctly.
// 释放掉n个页块 static void default_free_pages(struct Page *base, size_t n) { assert(n > 0); // 断言base位置的页被内核所保留 assert(PageReserved(base)); list_entry_t le = &free_list; struct Page *p = NULL; while((le=list_next(le)) != &free_list) { // 获取list对应的page p = le2page(le, page_link); if (p>base) { break; } } // 对每个页进行遍历 for (p = base; p < base + n; p ++) { // 将每个页插入到链表中 list_add_before(le, &(p->page_link)); } // //以下3行用于修改首个页的属性,仅修改首页属性即可 //base->flags = 0; //base->property = n; // 归还的块的首页仍然记录连续空闲页的数目,暂时为n //set_page_ref(p, 0); // 物理页应用数清空 //ClearPageProperty(page); // 先清零 //SetPageProperty(base); // 置1:所有空闲页第1位也就是PG_property位置为1 // 下面这几句话是有顺序的??? base->flags = 0; set_page_ref(base, 0); // 声明是头页 SetPageProperty(base); // 记录空闲页的数目n base->property = n; // 如果是高位,则向高地址合并(高书图8-5) p = le2page(le, page_link); if (p == base+n) { base->property = base->property + p->property; p->property = 0; } // 向低地址合并(高书图8-6) le = list_prev(&(base->page_link)); p = le2page(le, page_link); if (le != &free_list && p == base-1) { while (le != &free_list) { if (p->property > 0) { // p位于高地址,向低地址合并 p->property += base->property; base->property = 0; break; } p = le2page(le, page_link); le = list_prev(le); } } nr_free += n; }
请在实验报告中简要说明你的设计实现过程。请回答如下问题:
-
你的first fit算法是否有进一步的改进空间
first fit有多种实现方式,上面采用的是清华大学ucore参考答案的实现代码。由于free代码有四类情况,清华答案中是分成了两类(向高地址合并和向低地址合并)。还可以按高一凡书的方法进行free。
练习2:实现寻找虚拟地址对应的页表项(需要编程)
通过设置页表和对应的页表项,可建立虚拟内存地址和物理内存地址的对应关系。其中的get_pte函数是设置页表项环节中的一个重要步骤。此函数找到一个虚地址对应的二级页表项的内核虚地址,如果此二级页表项不存在,则分配一个包含此项的二级页表。本练习需要补全get_pte函数 in kern/mm/pmm.c,实现其功能。请仔细查看和理解get_pte函数中的注释。get_pte函数的调用关系图如下所示:
 图1 get_pte函数的调用关系图
图1 get_pte函数的调用关系图
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/3558942fe14f
在保护模式中,x86 体系结构将内存地址分成三种:逻辑地址(也称虚地址)、线性地址和物理地址。
逻辑地址即是程序指令中使用的地址,物理地址是实际访问内存的地址。
逻辑地址通过段式管理的地址映射可以得到线性地址,线性地址通过页式管理的地址映射得到物理地址。
逻辑地址 –> 线性地址 –>物理地址
对于32位线性地址,分为三个部分

页目录表(PDE) 页表(PTE)地址

在mmu.h中有定义说明:
// A linear address 'la' has a three-part structure as follows: // // +--------10------+-------10-------+---------12----------+ // | Page Directory | Page Table | Offset within Page | // | Index | Index | | // +----------------+----------------+---------------------+ // \--- PDX(la) --/ \--- PTX(la) --/ \---- PGOFF(la) ----/ // \----------- PPN(la) -----------/ // // The PDX, PTX, PGOFF, and PPN macros decompose(分解) linear addresses as shown. // To construct a linear address la from PDX(la), PTX(la), and PGOFF(la), // use PGADDR(PDX(la), PTX(la), PGOFF(la)). // page directory index // 得到一级页表项对应的入口地址 #define PDX(la) ((((uintptr_t)(la)) >> PDXSHIFT) & 0x3FF) // page table index #define PTX(la) ((((uintptr_t)(la)) >> PTXSHIFT) & 0x3FF) // page number field of address #define PPN(la) (((uintptr_t)(la)) >> PTXSHIFT) // offset in page #define PGOFF(la) (((uintptr_t)(la)) & 0xFFF)
根据LAZY,这里我们并没有一开始就存在所有的二级页表,而是等到需要的时候再添加对应的二级页表。
-
当建立从一级页表到二级页表的映射时,需要注意设置控制位。这里应该设置同时设置 上PTE_U、PTE_W 和 PTE_P(定义可在mm/mmu.h)。
/* page table/directory entry flags */ #define PTE_P 0x001 // Present #define PTE_W 0x002 // Writeable #define PTE_U 0x004 // User
-
如果原来就有二级页表,或者新建立了页表,则只需返回对应项的地址即可。
-
如果 create参数为 0,则get_pte返回NULL;如果 create参数不为 0,则 get_pte 需要申请一个新的物理页。
kern/mm/pmm.c::get_pte
//get_pte – get pte and return the kernel virtual address of this pte for la // – if the PT contians this pte didn’t exist, alloc a page for PT // parameter: // pgdir: the kernel virtual base address of PDT // la: the linear address need to map // create: a logical value to decide if alloc a page for PT // return vaule: the kernel virtual address of this pte
// 参考注释,它告诉你用哪些宏和函数可以帮助我们完成pte_t函数
-
pde_t 全称为page directory entry,也就是一级页表的表项(注意:pgdir实际不是表项,而是一级页表本身,pgdir给出页表起始地址(相当于数组名)。)
-
pte_t 全称为page table entry,表示二级页表的表项。
-
uintptr_t 表示为线性地址,由于段式管理只做直接映射,所以它也是逻辑地址。
-
PTE_U: 位3,表示用户态的软件可以读取对应地址的物理内存页内容 -
PTE_W: 位2,表示物理内存页内容可写 -
PTE_P: 位1,表示物理内存页存在
// 获取页表项的地址
pte_t *
get_pte(pde_t *pgdir, uintptr_t la, bool create) {
/* LAB2 EXERCISE 2: YOUR CODE
*
* If you need to visit a physical address, please use KADDR()
* please read pmm.h for useful macros
*
* Maybe you want help comment, BELOW comments can help you finish the code
*
* Some Useful MACROs and DEFINEs, you can use them in below implementation.
* MACROs or Functions:
* PDX(la) = the index of page directory entry of VIRTUAL ADDRESS la.
* KADDR(pa) : takes a physical address and returns the corresponding kernel virtual address.
* set_page_ref(page,1) : means the page be referenced by one time
* page2pa(page): get the physical address of memory which this (struct Page *) page manages
* struct Page * alloc_page() : allocation a page
* memset(void *s, char c, size_t n) : sets the first n bytes of the memory area pointed by s
* to the specified value c.
* DEFINEs:
* PTE_P 0x001 // page table/directory entry flags bit : Present
* PTE_W 0x002 // page table/directory entry flags bit : Writeable
* PTE_U 0x004 // page table/directory entry flags bit : User can access
*/
pde_t *pdep = &pgdir[PDX(la)]; // (1) find page directory entry
// 入口不存在
if (!(PTE_P & *pdep)) { // (2) check if entry is not present
struct Page *page = NULL;
// 不需要分配或申请新的页失败,返回NULL
if (!create || (page = alloc_page()) == NULL) { // (3) check if creating is needed, then alloc page for page table
return NULL; // CAUTION: this page is used for page table, not for common data page
}
// 到这里,如果是需要申请新的页的话一定执行过了alloc_page()函数
// 设置引用数目
set_page_ref(page,1); // (4) set page reference
// 得到该物理页的地址
uintptr_t pa = page2pa(page); // (5) get linear address of page
// 物理地址转为虚拟地址
// If you need to visit a physical address, please use KADDR()
// KADDR(pa)将物理地址转换为内核虚拟地址,第二个参数将这一页清空,第三个参数是4096也就是一页的大小
memset(KADDR(pa), 0, PGSIZE); // (6) clear page content using memset
// 页目录项内容 = (页表起始物理地址 &0x0FFF) | PTE_U | PTE_W | PTE_P
*pdep = pa | PTE_U | PTE_W | PTE_P; // (7) set page directory entry's permission(许可)
}
// KADDR(PDE_ADDR(*pdep)):这部分是由页目录项地址得到关联的页表物理地址, 再转成虚拟地址
// PTX(la):返回虚拟地址la的页表项索引
// 最后返回的是虚拟地址la对应的页表项入口地址
// 这里不是很懂???
// 害,不懂就ctrl f找找其他函数是怎么返回的
return &((pte_t *)KADDR(PDE_ADDR(*pdep)))[PDX(la)];
//return NULL; // (8) return page table entry
}
请在实验报告中简要说明你的设计实现过程。请回答如下问题:
请描述页目录项(Pag Director Entry)和页表(Page Table Entry)中每个组成部分的含义和以及对ucore而言的潜在用处。
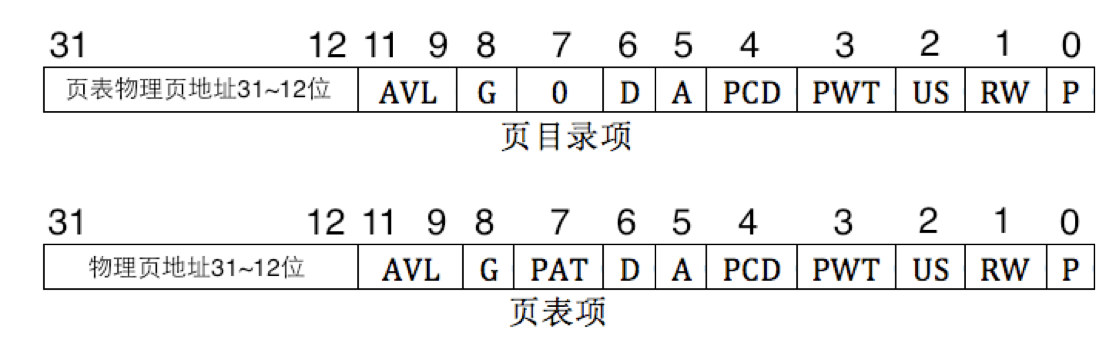
pde(页目录项)的各个组成部分为:
-
A, D, W:这些与高速缓存相关的位,记录该页是否被访问过、不允许高速缓存过或执行了写穿透策略。如果uCore需要与硬件的cache进行交互(即这些位并非由硬件设定),就需要用到这些位。
-
US:决定了当前页的访问权限(内核or用户):uCore可以通过这些位进行用户态和内核态程序访问权限的控制。
-
RW:决定了当前页的是否可写属性:当uCore需要对某一页进行保护的时候,需要用到此位,用于权限控制。
-
P:决定当前页是否存在:uCore需要根据这个标志确定页表是否存在,并是否建立新的相关页表。
pte(页表项)的各个组成部分为:
-
PCD:与上述的D位相同。
-
G:控制TLB地址的更新策略。
-
D:该页是否被写过。如果uCore需要对高速缓存实现更复杂的控制则可能用到该位。同时,在页换入或是换出的时候可能需要判断是否更新高速缓存。
-
P:决定是否存在。
具体还可以参考X86手册。
如果ucore执行过程中访问内存,出现了页访问异常,请问硬件要做哪些事情?
练习3:释放某虚地址所在的页并取消对应二级页表项的映射(需要编程)
当释放一个包含某虚地址的物理内存页时,需要让对应此物理内存页的管理数据结构Page做相关的清除处理,使得此物理内存页成为空闲;另外还需把表示虚地址与物理地址对应关系的二级页表项清除。请仔细查看和理解page_remove_pte函数中的注释。为此,需要补全在 kern/mm/pmm.c中的page_remove_pte函数。page_remove_pte函数的调用关系图如下所示:
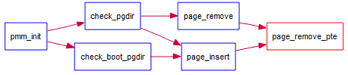
图2 page_remove_pte函数的调用关系图
pmm.c::page_remove_pte
//page_remove_pte - free an Page sturct which is related linear address la
// - and clean(invalidate) pte which is related linear address la
//note: PT is changed, so the TLB need to be invalidate
static inline void
page_remove_pte(pde_t *pgdir, uintptr_t la, pte_t *ptep) {
/* LAB2 EXERCISE 3: YOUR CODE
*
* Please check if ptep is valid, and tlb must be manually updated if mapping is updated
*
* Maybe you want help comment, BELOW comments can help you finish the code
*
* Some Useful MACROs and DEFINEs, you can use them in below implementation.
* MACROs or Functions:
* struct Page *page pte2page(*ptep): get the according page from the value of a ptep
* free_page : free a page
* page_ref_dec(page) : decrease page->ref. NOTICE: ff page->ref == 0 , then this page should be free.
* tlb_invalidate(pde_t *pgdir, uintptr_t la) : Invalidate a TLB entry, but only if the page tables being
* edited are the ones currently in use by the processor.
* DEFINEs:
* PTE_P 0x001 // page table/directory entry flags bit : Present
*/
#if 0
if (PTE_P & *ptep) { //(1) check if this page table entry is present
struct Page *page = pte2page(*ptep); //(2) find corresponding page to pte
if (page_ref_dec(page) == 0) { //(3) decrease page reference
free_page(page);
}
*ptep = 0; //(4) and free this page when page reference reachs 0(归零)
tlb_invalidate(pgdir, la); //(5) clear second page table entry
//(6) flush tlb
}
#endif
}
注释已经写得很明白了,参考注释一步步就能写出来。
请在实验报告中简要说明你的设计实现过程。请回答如下问题:
-
数据结构Page的全局变量(其实是一个数组)的每一项与页表中的页目录项和页表项有无对应关系?如果有,其对应关系是啥?
memlayout.h:
/* * * struct Page - Page descriptor structures. Each Page describes one * physical page. In kern/mm/pmm.h, you can find lots of useful functions * that convert Page to other data types, such as phyical address. * */ struct Page { int ref; // page frame's reference counter uint32_t flags; // array of flags that describe the status of the page frame unsigned int property; // the num of free block, used in first fit pm manager list_entry_t page_link; // free list link }; /* Flags describing the status of a page frame */ #define PG_reserved 0 // if this bit=1: the Page is reserved for kernel, cannot be used in alloc/free_pages; otherwise, this bit=0 #define PG_property 1 // if this bit=1: the Page is the head page of a free memory block(contains some continuous_addrress pages), and can be used in alloc_pages; if this bit=0: if the Page is the the head page of a free memory block, then this Page and the memory block is alloced. Or this Page isn't the head page. #define SetPageReserved(page) set_bit(PG_reserved, &((page)->flags)) #define ClearPageReserved(page) clear_bit(PG_reserved, &((page)->flags)) #define PageReserved(page) test_bit(PG_reserved, &((page)->flags)) #define SetPageProperty(page) set_bit(PG_property, &((page)->flags)) #define ClearPageProperty(page) clear_bit(PG_property, &((page)->flags)) #define PageProperty(page) test_bit(PG_property, &((page)->flags))有对应关系,例如 PG_reserved 表示是否被内核所保留,与页表项的 PTE_U 有关联,PTE_U 表示用户态是否可访问。
-
如果希望虚拟地址与物理地址相等,则需要如何修改lab2,完成此事? 鼓励通过编程来具体完成这个问题
练习0、1、2、3全部写好后,运行效果如图:

参考文献
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_19876131/article/details/51706978
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000009450840
https://yuerer.com/%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F-uCore-Lab-2/
https://twinkle0331.github.io/ucore-lab2.html
https://wenku.baidu.com/view/a0d3f514a45177232e60a273.html
https://blog.csdn.net/tangyuanzong/article/details/78913388
http://blog.gqylpy.com/gqy/24219/
https://blog.csdn.net/tangyuanzong/java/article/details/78913388